Pytorch 编译流程解析
Categories: Framework_analysis
1. 解析 setup.py 中 main 函数流程
在 setup.py 中,最主要的是调用 setuptools.setup() 函数,它是 Python 中 setuptools 模块的核心,用于定义 Python 包的元数据、依赖关系和构建流程。pytorch/setup.py 在 main() 函数中调用了 setup() 函数。
setup 的函数参数有很多个,主要分为以下类型:
- 基础参数:定义包元数据:包名称
name、版本号version、简要描述 description、作者 author、项目主页 url、子包 packages、依赖的第三方库 install_requires、长描述 long_description 等。 - 扩展模块参数
ext_modules:编译C++/CUDA代码。 - 自定义构建流程
cmdclass:覆盖默认命令。
这里对其进行了注释如下所示:
setup(
# -------------------------------------------
# 1. 基础信息
# -------------------------------------------
name=package_name, # 包名,在 PyPI 或安装时用于标识该包,比如 "torch"
version=version, # 包版本号,通常遵循语义化版本(如 1.0.0)
description=( # 简短描述,会显示在 PyPI 中的标题描述
"Tensors and Dynamic neural networks in Python with strong GPU acceleration"
),
long_description=long_description, # 包的详细描述,通常从 README.md 中读取,可在 PyPI 上显示更丰富内容
long_description_content_type="text/markdown", # 指定 long_description 的格式,这里是 Markdown
# -------------------------------------------
# 2. 编译和构建相关
# -------------------------------------------
ext_modules=extensions, # 需要编译的 C/C++ 扩展模块列表(如 pybind11、Cython 等)
cmdclass=cmdclass, # 自定义构建/安装命令的类映射,覆盖默认的 build_ext 等逻辑
# -------------------------------------------
# 3. Python 包及入口点
# -------------------------------------------
packages=packages, # 要被打包的 Python 包列表,通常由 find_packages() 获取
entry_points=entry_points,# 安装包时可注册命令行可执行入口,如 console_scripts
# -------------------------------------------
# 4. 依赖和可选依赖
# -------------------------------------------
install_requires=install_requires, # 安装该包时必须安装的依赖库列表
extras_require=extras_require, # 可选依赖项:用户可通过 "pip install package[extra]" 安装
# -------------------------------------------
# 5. 包含的文件/资源
# -------------------------------------------
package_data=package_data, # 指定需要包含在包内的额外文件(如头文件、.so/.dll、.cmake等)
# 与实际的 Python 源码一起打包发布
# -------------------------------------------
# 6. 版权、主页及其他元数据
# -------------------------------------------
url="https://pytorch.org/", # 包对应的项目网址,会在 PyPI 上显示
download_url="https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/tags", # 包源码下载地址
author="PyTorch Team", # 作者姓名
author_email="packages@pytorch.org",# 作者联系邮箱
# -------------------------------------------
# 7. Python 版本和分类器
# -------------------------------------------
python_requires=f">={python_min_version_str}", # 指定兼容的最低 Python 版本,比如 ">=3.6"
classifiers=[
# PyPI 上展示的分类器,可帮助其他人快速了解该库的适用范围、状态和许可证等
"Development Status :: 5 - Production/Stable",
"Intended Audience :: Developers",
"Intended Audience :: Education",
"Intended Audience :: Science/Research",
"License :: OSI Approved :: BSD License",
"Topic :: Scientific/Engineering",
"Topic :: Scientific/Engineering :: Mathematics",
"Topic :: Scientific/Engineering :: Artificial Intelligence",
"Topic :: Software Development",
"Topic :: Software Development :: Libraries",
"Topic :: Software Development :: Libraries :: Python Modules",
"Programming Language :: C++",
"Programming Language :: Python :: 3",
]
+ [
# 额外添加 "Programming Language :: Python :: 3.X" 的分类器
f"Programming Language :: Python :: 3.{i}"
for i in range(python_min_version[1], version_range_max)
],
# -------------------------------------------
# 8. 许可证与关键词
# -------------------------------------------
license="BSD-3-Clause", # 指定许可证,这里为 BSD-3-Clause
keywords="pytorch, machine learning", # 关键词,用于 PyPI 搜索
)
main() 函数的流程图如下所示:
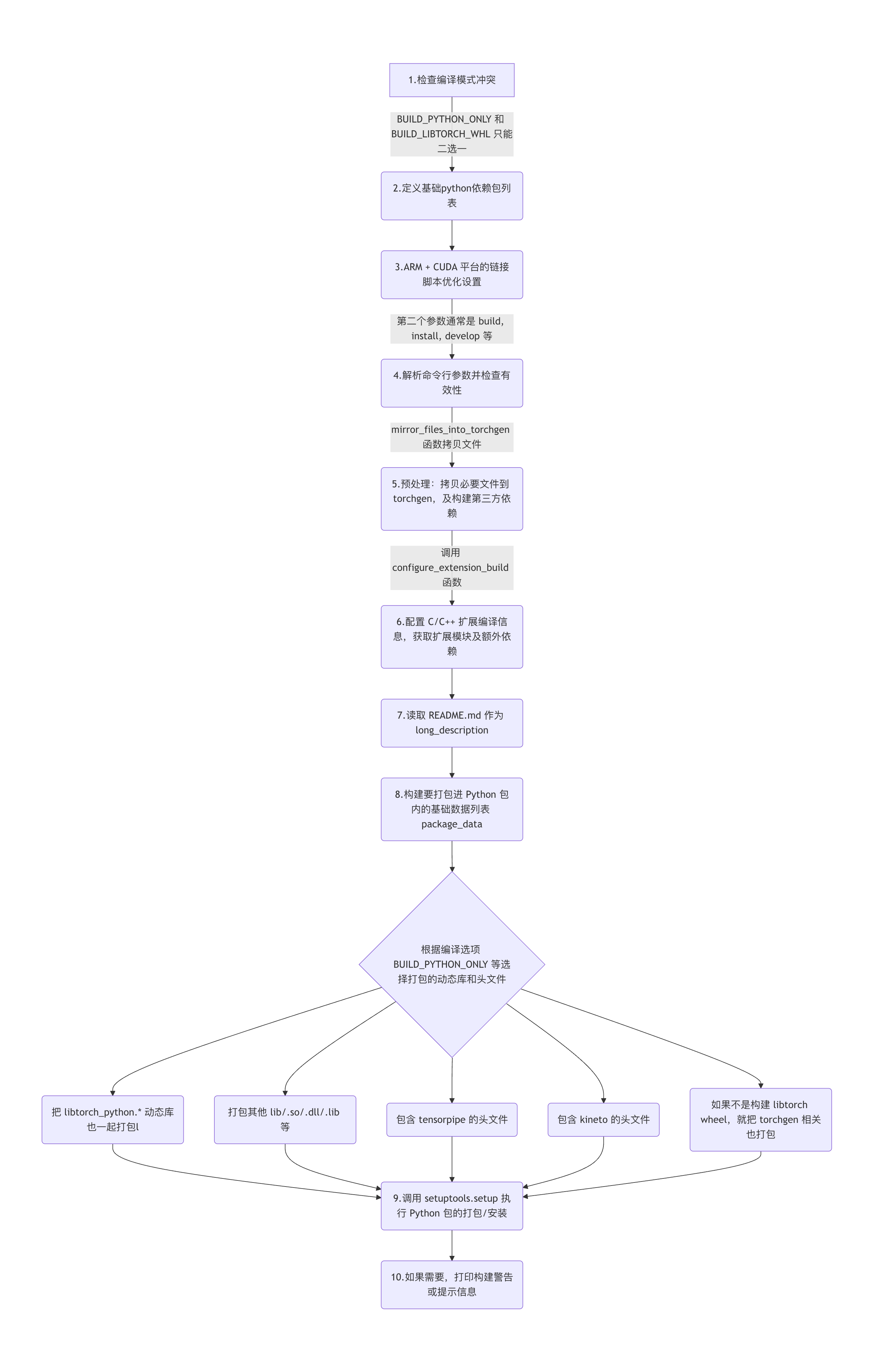
flowchart TD
A[1.检查编译模式冲突] -->|BUILD_PYTHON_ONLY 和 BUILD_LIBTORCH_WHL 只能二选一| B(2.定义基础python依赖包列表)
B --> C(3.ARM + CUDA 平台的链接脚本优化设置)
C --> |第二个参数通常是 build, install, develop 等| D(4.解析命令行参数并检查有效性)
D --> |mirror_files_into_torchgen 函数拷贝文件| E(5.预处理:拷贝必要文件到 torchgen,及构建第三方依赖)
E --> |调用 configure_extension_build 函数| F(6.配置 C/C++ 扩展编译信息,获取扩展模块及额外依赖)
F --> G(7.读取 README.md 作为 long_description)
G --> H(8.构建要打包进 Python 包内的基础数据列表 package_data)
H --> S{根据编译选项 BUILD_PYTHON_ONLY 等选择打包的动态库和头文件}
S --> J1(把 libtorch_python.* 动态库也一起打包l)
S --> J2(打包其他 lib/.so/.dll/.lib 等)
S --> J3(包含 tensorpipe 的头文件)
S --> J4(包含 kineto 的头文件)
S --> J5(如果不是构建 libtorch wheel,就把 torchgen 相关也打包)
J1 --> I(9.调用 setuptools.setup 函数执行 Python 包的打包/安装)
J2 --> I(9.调用 setuptools.setup 执行 Python 包的打包/安装)
J3 --> I(9.调用 setuptools.setup 执行 Python 包的打包/安装)
J4 --> I(9.调用 setuptools.setup 执行 Python 包的打包/安装)
J5 --> I(9.调用 setuptools.setup 执行 Python 包的打包/安装)
I --> J(10.如果需要,打印构建警告或提示信息)
package_data 是存放要包含在 ‘torch’ 包中的文件(二进制文件、头文件、cmake脚本等),分两种情况:
- 如果不是构建 libtorch wheel,就把 libtorch_python.* 动态库也一起打包;
- 如果不是纯 Python 构建,那么还要包含其他 .so/.dll/.lib 等;
- 如果开启 USE_TENSORPIPE,就把 tensorpipe 的头文件也包含进来;
- 如果开启 USE_KINETO,就把 kineto 的头文件也包含进来。
- 若不是构建 libtorch wheel,就把 torchgen 相关也打包;否则不包含扩展
为了更方便理解 main 函数流程,我对 torch/setup.py 的 main 做了简化并添加注释,代码如下所示:
def main():
# --------------------------------------------------------------
# 1. 检查编译模式冲突
# --------------------------------------------------------------
# 如果指定了同时只构建 Python 部分 (BUILD_PYTHON_ONLY)
# 和构建 libtorch wheel 包 (BUILD_LIBTORCH_WHL),两者互斥,抛出异常
if BUILD_LIBTORCH_WHL and BUILD_PYTHON_ONLY:
raise RuntimeError(
"Conflict: 'BUILD_LIBTORCH_WHL' and 'BUILD_PYTHON_ONLY' can't both be 1. Set one to 0 and rerun."
)
# --------------------------------------------------------------
# 2. 定义基础依赖列表
# --------------------------------------------------------------
# 安装 PyTorch 时需要安装的 Python 包依赖
install_requires = [
"filelock",
"typing-extensions>=4.10.0",
'setuptools ; python_version >= "3.12"',
"sympy>=1.13.3",
"networkx",
"jinja2",
"fsspec",
]
# 如果只构建 Python,那么需要对应的 libtorch 包
if BUILD_PYTHON_ONLY:
install_requires.append(f"{LIBTORCH_PKG_NAME}=={get_torch_version()}")
# --------------------------------------------------------------
# 3. ARM + CUDA 平台的链接脚本优化设置
# --------------------------------------------------------------
use_prioritized_text = str(os.getenv("USE_PRIORITIZED_TEXT_FOR_LD", ""))
# 如果在 Linux + AArch64 上未设置 USE_PRIORITIZED_TEXT_FOR_LD,就提示一下优化策略
if (
use_prioritized_text == ""
and platform.system() == "Linux"
and platform.processor() == "aarch64"
):
print_box(
"""
WARNING: we strongly recommend enabling linker script optimization for ARM + CUDA.
To do so please export USE_PRIORITIZED_TEXT_FOR_LD=1
"""
)
# 如果启用 USE_PRIORITIZED_TEXT_FOR_LD,则调用脚本生成链接脚本并注入编译/链接选项
if use_prioritized_text == "1" or use_prioritized_text == "True":
gen_linker_script(
filein="cmake/prioritized_text.txt", fout="cmake/linker_script.ld"
)
linker_script_path = os.path.abspath("cmake/linker_script.ld")
os.environ["LDFLAGS"] = os.getenv("LDFLAGS", "") + f" -T{linker_script_path}"
os.environ["CFLAGS"] = (
os.getenv("CFLAGS", "") + " -ffunction-sections -fdata-sections"
)
os.environ["CXXFLAGS"] = (
os.getenv("CXXFLAGS", "") + " -ffunction-sections -fdata-sections"
)
# --------------------------------------------------------------
# 4. 解析命令行参数并检查有效性
# --------------------------------------------------------------
# Distribution 对象可解析命令行参数 (如 build, install, sdist, bdist_wheel 等)
dist = Distribution()
dist.script_name = os.path.basename(sys.argv[0])
dist.script_args = sys.argv[1:]
try:
dist.parse_command_line()
except setuptools.distutils.errors.DistutilsArgError as e:
print(e)
sys.exit(1)
# --------------------------------------------------------------
# 5. 预处理:拷贝必要文件到 torchgen,及构建第三方依赖
# --------------------------------------------------------------
mirror_files_into_torchgen()
if RUN_BUILD_DEPS:
build_deps()
# --------------------------------------------------------------
# 6. 配置 C/C++ 扩展编译信息,获取扩展模块及额外依赖
# --------------------------------------------------------------
(
extensions,
cmdclass,
packages,
entry_points,
extra_install_requires,
) = configure_extension_build()
# 将额外依赖追加到基础依赖中
install_requires += extra_install_requires
# 扩展依赖项(可选安装),比如 pip install torch[optree]
extras_require = {
"optree": ["optree>=0.13.0"],
"opt-einsum": ["opt-einsum>=3.3"],
}
########## 读取 README.md 作为 long_description的代码省略 ##########
# --------------------------------------------------------------
# 7. 构建要打包进 Python 包内的数据列表(package_data)
# --------------------------------------------------------------
# version_range_max 用于动态生成 Python 版本兼容的分类器
version_range_max = max(sys.version_info[1], 13) + 1
# torch_package_data 存放要包含在 'torch' 包中的文件(二进制文件、头文件、cmake脚本等)
torch_package_data = [
"py.typed",
"bin/*",
"test/*",
"*.pyi",
"**/*.pyi",
"lib/*.pdb",
"lib/**/*.pdb",
"lib/*shm*",
"lib/torch_shm_manager",
"lib/*.h",
"lib/**/*.h",
"include/*.h",
"include/**/*.h",
"include/*.hpp",
"include/**/*.hpp",
"include/*.cuh",
"include/**/*.cuh",
"_inductor/codegen/*.h",
"_inductor/codegen/aoti_runtime/*.cpp",
"_inductor/script.ld",
"_export/serde/*.yaml",
"_export/serde/*.thrift",
"share/cmake/ATen/*.cmake",
"share/cmake/Caffe2/*.cmake",
"share/cmake/Caffe2/public/*.cmake",
"share/cmake/Caffe2/Modules_CUDA_fix/*.cmake",
"share/cmake/Caffe2/Modules_CUDA_fix/upstream/*.cmake",
"share/cmake/Caffe2/Modules_CUDA_fix/upstream/FindCUDA/*.cmake",
"share/cmake/Gloo/*.cmake",
"share/cmake/Tensorpipe/*.cmake",
"share/cmake/Torch/*.cmake",
"utils/benchmark/utils/*.cpp",
"utils/benchmark/utils/valgrind_wrapper/*.cpp",
"utils/benchmark/utils/valgrind_wrapper/*.h",
"utils/model_dump/skeleton.html",
"utils/model_dump/code.js",
"utils/model_dump/*.mjs",
]
##########################省略部分代码############################
# 若不是构建 libtorch wheel,就把 torchgen 相关也打包;否则不包含扩展
if not BUILD_LIBTORCH_WHL: # BUILD_LIBTORCH_WHL 默认为 0
package_data["torchgen"] = torchgen_package_data
else:
# 在 BUILD_LIBTORCH_WHL 模式下,不需要构建Python C/C++扩展
extensions = []
# --------------------------------------------------------------
# 8. 调用 setuptools.setup() 执行 Python 包的打包/安装
# --------------------------------------------------------------
setup(
name=package_name,
version=version,
description=(
"Tensors and Dynamic neural networks in Python with strong GPU acceleration"
),
ext_modules=extensions, # C/C++ 扩展模块
cmdclass=cmdclass, # 自定义构建命令
packages=packages, # 包含的Python包
entry_points=entry_points, # 可执行入口
install_requires=install_requires,
extras_require=extras_require,
package_data=package_data,
url="https://pytorch.org/",
download_url="https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/tags",
author="PyTorch Team",
author_email="packages@pytorch.org",
python_requires=f">={python_min_version_str}",
# classifiers 列表和 long_description 代码省略
license="BSD-3-Clause",
keywords="pytorch, machine learning",
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
2. configure_extension_build 函数流程
configure_extension_build 函数用于配置并生成构建和安装 PyTorch C/C++ 扩展模块所需要的关键参数:
ext_modules:列表,用于定义 C/C++ 扩展模块,以便在安装时通过 setuptools 构建和编译这些模块。cmdclass: 字典,自定义命令,用于在安装过程中执行一些额外的操作(例如:编译其他资源、运行脚本等)。packages: 列表,用于指定要包含在安装包中的 Python 包,每个元素是一个包的名称或包路径。entry_points: 字典,通常用于指定可执行脚本或插件系统的入口点。extra_install_requires: 字典,当想实现特定功能时,用此参数来定义可选的额外依赖项
configure_extension_build 函数流程如下所示:
configure_extension_build()
├─ 读取 CMake 缓存变量 (cmake_cache_vars)
├─ 配置编译选项
│ ├─ 从 CMakeCache.txt 或相关上下文中获取编译配置选项
│ ├─ 根据操作系统设置编译/链接参数
│ ├─ 处理调试/发布模式标志
│ ├─ 处理 macOS 交叉编译选项
│ └─ 定义辅助函数,生成传给链接器(linker)的 -rpath 参数
├─ 声明扩展模块和包
│ ├─ 排除不编译的目录 (caffe2/tools)
│ ├─ 创建主扩展模块 (torch._C)
│ └─ 条件添加 functorch 扩展
├─ 定义自定义构建命令 (cmdclass)
├─ 配置入口点 (console_scripts)
└─ 返回配置参数
rpath(runtime search path)是一个在运行时指定动态库搜索路径的机制,让可执行文件或共享库知道去哪里寻找依赖的其它动态库。默认情况下,系统会在标准路径(如 /usr/lib, /usr/local/lib)或在由 LD_LIBRARY_PATH(或 macOS 的 DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH)等环境变量中指定的路径里查找;
configure_extension_build 注释后的代码如下所示:
def configure_extension_build():
r"""
配置 PyTorch C/C++ 扩展构建选项,并返回给 setuptools.setup(...) 所需的部分参数。
Returns:
5 个元素组成的元组:
(extensions, cmdclass, packages, entry_points, extra_install_requires)
"""
# 从 CMakeCache.txt 或相关上下文中获取编译配置选项
cmake_cache_vars = get_cmake_cache_vars()
################################################################################
# 1. 设置编译标志与链接标志的基础配置
################################################################################
library_dirs = []
extra_install_requires = []
# 根据平台选择不同编译/链接选项
if IS_WINDOWS:
# /NODEFAULTLIB:LIBCMT.LIB - 指定只链接 DLL 版运行时
extra_link_args = ["/NODEFAULTLIB:LIBCMT.LIB"]
# /MD - 使用动态运行时库,/FS - 并行写PDB,/EHsc - 启用标准C++异常处理
extra_compile_args = ["/MD", "/FS", "/EHsc"]
else:
extra_link_args = []
extra_compile_args = [
"-Wall",
"-Wextra",
"-Wno-strict-overflow",
"-Wno-unused-parameter",
"-Wno-missing-field-initializers",
"-Wno-unknown-pragmas",
# -fno-strict-aliasing 可兼容早期 Python(2.6),避免代码对别名优化敏感
"-fno-strict-aliasing",
]
# 将编译后生成的库路径加入 library_dirs,以便链接
library_dirs.append(lib_path)
main_compile_args = []
main_libraries = ["torch_python"] # 默认链接到 torch_python 库
main_link_args = []
main_sources = ["torch/csrc/stub.c"] # 默认源文件
# 如果是只构建 libtorch wheel,则不需要 torch_python,而是链接 "torch"
# 并且 stub.c 也不使用
if BUILD_LIBTORCH_WHL:
main_libraries = ["torch"]
main_sources = []
# 处理 Debug / RelWithDebInfo 模式下的编译、链接标志
if build_type.is_debug():
if IS_WINDOWS:
extra_compile_args.append("/Z7") # 生成完整调试信息
extra_link_args.append("/DEBUG:FULL") # 链接时也生成 pdb 等
else:
extra_compile_args += ["-O0", "-g"] # 不优化并生成调试信息
extra_link_args += ["-O0", "-g"]
if build_type.is_rel_with_deb_info():
if IS_WINDOWS:
extra_compile_args.append("/Z7")
extra_link_args.append("/DEBUG:FULL")
else:
extra_compile_args += ["-g"]
extra_link_args += ["-g"]
# 额外 Python 依赖:若环境变量 PYTORCH_EXTRA_INSTALL_REQUIREMENTS 有值,就拆分并加入
pytorch_extra_install_requirements = os.getenv("PYTORCH_EXTRA_INSTALL_REQUIREMENTS", "")
if pytorch_extra_install_requirements:
report(f"pytorch_extra_install_requirements: {pytorch_extra_install_requirements}")
extra_install_requires += pytorch_extra_install_requirements.split("|")
# macOS 交叉编译配置:若 CMAKE_OSX_ARCHITECTURES 指定为 arm64 或 x86_64 等
if IS_DARWIN:
macos_target_arch = os.getenv("CMAKE_OSX_ARCHITECTURES", "")
if macos_target_arch in ["arm64", "x86_64"]:
macos_sysroot_path = os.getenv("CMAKE_OSX_SYSROOT")
if macos_sysroot_path is None:
# 调用 xcrun --show-sdk-path 来获取macOS的sysroot
macos_sysroot_path = (
subprocess.check_output(["xcrun", "--show-sdk-path", "--sdk", "macosx"])
.decode("utf-8")
.strip()
)
# 为编译/链接追加 -arch 和 -isysroot 参数,以匹配目标架构
extra_compile_args += [
"-arch", macos_target_arch,
"-isysroot", macos_sysroot_path,
]
extra_link_args += ["-arch", macos_target_arch]
# 定义一个辅助函数,用于生成相对路径的 rpath 参数
def make_relative_rpath_args(path):
if IS_DARWIN:
# macOS 下可使用 @loader_path
return [f"-Wl,-rpath,@loader_path/{path}"]
elif IS_WINDOWS:
# Windows 下不使用 rpath
return []
else:
# Linux 下用 $ORIGIN
return [f"-Wl,-rpath,$ORIGIN/{path}"]
################################################################################
# 2. 声明扩展模块和 Python 包
################################################################################
extensions = []
# exclude 某些不需要作为 Python 包的目录
excludes = ["tools", "tools.*", "caffe2", "caffe2.*"]
# 若未开启 BUILD_FUNCTORCH,则排除 functorch 包
if not cmake_cache_vars["BUILD_FUNCTORCH"]:
excludes.extend(["functorch", "functorch.*"])
# 使用 find_packages 排除上述目录,获取最终要打包的 Python 包列表
packages = find_packages(exclude=excludes)
# 定义主扩展模块: torch._C
C = Extension(
"torch._C", # 模块的全名, 安装后可通过 torch._C 导入核心
libraries=main_libraries, # 链接所依赖的库名列表
sources=main_sources, # 源文件列表,编译这些文件生成模块
language="c", # 指定语言,决定使用哪种编译器
extra_compile_args=main_compile_args + extra_compile_args, # 编译时传递的额外命令行参数
include_dirs=[], # 头文件搜索路径
library_dirs=library_dirs, # 库文件搜索路径
extra_link_args=( # 链接时传递的额外命令行参数,通常用于设置 rpath 等
extra_link_args
+ main_link_args
+ make_relative_rpath_args("lib") # rpath 配置
),
)
extensions.append(C)
# 如果编译 functorch,则再添加一个 functorch._C 占位扩展(由外部CMake完成实际构建并复制)
if cmake_cache_vars["BUILD_FUNCTORCH"]:
extensions.append(
Extension(name="functorch._C", sources=[]),
)
# 自定义命令类,用于替换默认的 setuptools build_ext、bdist_wheel 等
cmdclass = {
"bdist_wheel": wheel_concatenate,
"build_ext": build_ext,
"clean": clean,
"install": install,
"sdist": sdist,
}
# 定义 Python 的命令行入口点
entry_points = {
"console_scripts": [
"torchrun = torch.distributed.run:main", # 安装后可使用 torchrun 命令
],
"torchrun.logs_specs": [
"default = torch.distributed.elastic.multiprocessing:DefaultLogsSpecs",
],
}
# 若编译开启分布式,则把 torchfrtrace 脚本也加入 console_scripts
if cmake_cache_vars["USE_DISTRIBUTED"]:
entry_points["console_scripts"].append(
"torchfrtrace = tools.flight_recorder.fr_trace:main",
)
# ----------------------------------------------------------------
# 在返回之前,使用 logger.info() 打印当前生成的各参数
# ----------------------------------------------------------------
logger.info("=== configure_extension_build Results ===")
logger.info("extensions: %s", extensions)
logger.info("cmdclass: %s", cmdclass)
logger.info("packages: %s", packages)
logger.info("entry_points: %s", entry_points)
logger.info("extra_install_requires: %s", extra_install_requires)
logger.info("=========================================")
# 最后将上述配置统一返回
return extensions, cmdclass, packages, entry_points, extra_install_requires
上述代码看起来内容很多,其实最核心最本质的代码就是定义主拓展模块那部分代码:
# 定义主扩展模块: torch._C
C = Extension(
"torch._C", # 模块的全名, 安装后可通过 torch._C 导入
libraries=main_libraries, # 链接所依赖的库名列表
sources=main_sources, # 源文件列表,编译这些文件生成模块
language="c", # 指定语言,决定使用哪种编译器
extra_compile_args=main_compile_args + extra_compile_args, # 编译时传递的额外命令行参数
include_dirs=[], # 头文件搜索路径
library_dirs=library_dirs, # 库文件搜索路径
extra_link_args=( # 链接时传递的额外命令行参数,通常用于设置 rpath 等
extra_link_args
+ main_link_args
+ make_relative_rpath_args("lib") # rpath 配置
),
)
extensions.append(C)
library_dirs 存放了编译后生成的库路径,其涉及到的代码如下所示:
lib_path = os.path.join(cwd, "torch", "lib")
library_dirs.append(lib_path)
pytorch/torch/lib 目录主要用于存放代码构建后生成的本地动态库(也称为共享库),这些库构成了 PyTorch 的核心 C++ 后端。即这个目录的文件是用来实现张量计算、自动微分、设备管理、分布式训练等功能的二进制代码,它们通过 Python 的扩展机制(例如 _C 模块)与 Python 层进行连接和交互。
extensions, cmdclass, packages, entry_points 打印后的内容如下所示:
INFO:__main__:=== configure_extension_build Results ===
INFO:__main__:extensions: [<setuptools.extension.Extension('torch._C') at 0x100db26c0>, <setuptools.extension.Extension('functorch._C') at 0x100b2b0e0>]
INFO:__main__:cmdclass: {'bdist_wheel': <class '__main__.wheel_concatenate'>, 'build_ext': <class '__main__.build_ext'>, 'clean': <class '__main__.clean'>, 'install': <class '__main__.install'>, 'sdist': <class '__main__.sdist'>}
INFO:__main__:packages: ['torch', 'torchgen', 'functorch', 'torch.monitor', 'torch._dispatch', 'torch._custom_op', 'torch.nn', 'torch.mps', 'torch.onnx', 'torch.cpu', \
'torch.distributed', 'torch.autograd', 'torch.profiler', 'torch.sparse', 'torch._awaits', 'torch.export', 'torch.compiler', 'torch.distributions', 'torch.package', 'torch.func', \
'torch.nn.attention', 'torch.nn.parallel', 'torch.nn.qat', 'torch.nn.quantized', 'torch.nn.backends', 'torch.nn.utils', 'torch.nn.quantizable', 'torch.nn.intrinsic', 'torch.nn.modules','torch.utils.tensorboard', \
'torch.nn.qat.*', 'torch.nn.quantized.*', 'torch.nn.*', 'torch.fx.*, 'torch.utils.*']
INFO:__main__:entry_points: {'console_scripts': ['torchrun = torch.distributed.run:main', 'torchfrtrace = tools.flight_recorder.fr_trace:main'], 'torchrun.logs_specs': ['default = torch.distributed.elastic.multiprocessing:DefaultLogsSpecs']}
INFO:__main__:extra_install_requires: []
INFO:__main__:=========================================
为了方便阅读 packages 内容手动做了简化,上述的内容是简化后的信息。
- torch.fx.* 和 torch.nn.quantized.* 做了省略,表示 torch.fx 和 torch.nn.quantized 相关模块;
- torch.nn.qat.* 表示训练中量化功能涉及到的相关模块。torch.nn.* 表示神经网络模块相关;
- torch.utils.* 表示 torch 接口功能相关模块